Purpose: If you WordPress website is hacked or infected malware, you may try to follow this guide for Malware Removal, and Recover your Hacked WordPress website.
Disclaimer: The information on this site is for information only. Whilst we endeavor to ensure the accuracy of the information, no express or implied warranty is given by RecoverWP.com as to the accuracy of the information.
For best hack recovery experience, you are recommended to contact us for a malware removal service
1. Backup your website files, and database
Backup is very important. Whenever something wrong, possible to restore, to fall back, or extract it to reference.
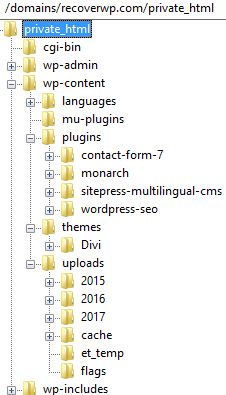
A WordPress website contains files, and its database.
Themes usually located at ./wp-content/themes/
Plugins usually located at ./wp-content/plugins/
Your uploaded files (e.g. jpg, gif, …) located at wp-content/uploads/YYYY/MM/ (YYYY = year, MM = month)
Total file size mainly depends on your uploaded files (may be hundred Megabytes, or in Gigabytes), plus a few Megabytes used by themes/plugins
You can use FTP to download all files.
Most of the website control panel allows you to zip download website files (which is faster and more reliable than FTP download).
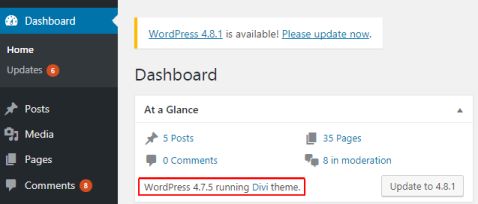
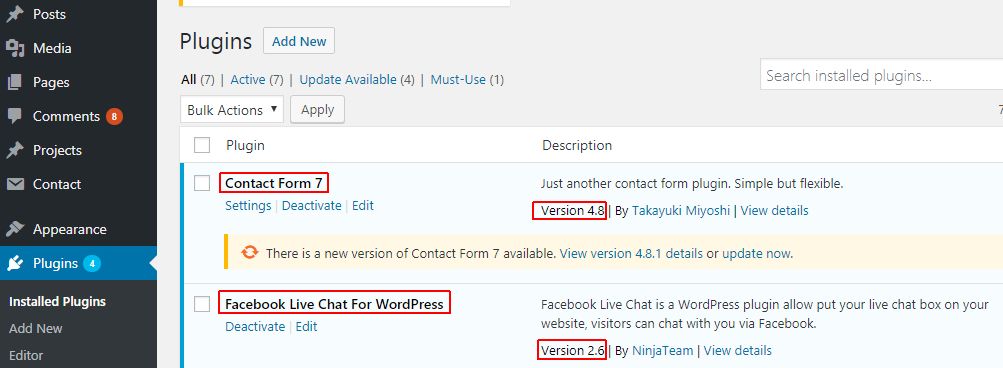
2. Capture your WordPress version, list of themes, list of plugins.
3. Move your WordPress files to separate folder
4. Install a new WordPress (preferably the same version for best compatibility)
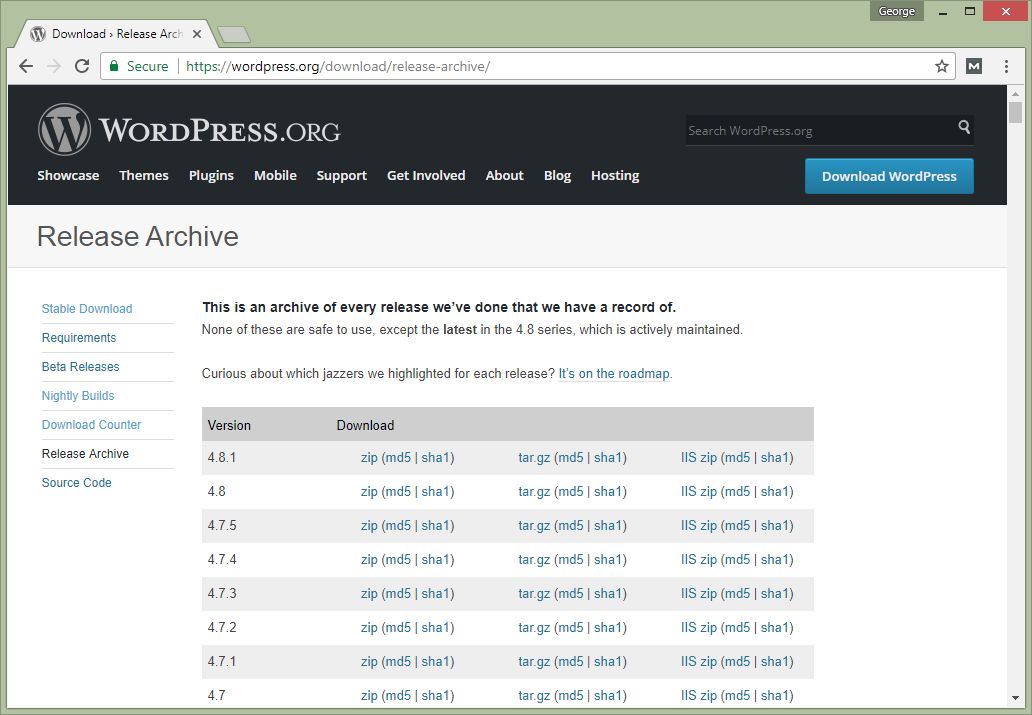
For compatibility reason, it’d better to install a new WordPress installation with the same version as existing one.
You can download specific WordPress version at https://wordpress.org/download/release-archive/.
Download it, upload the zip, most File Managers inside web control panel support online zip extraction, and proceed the installation.
(Please use a new MySQL database for installation)
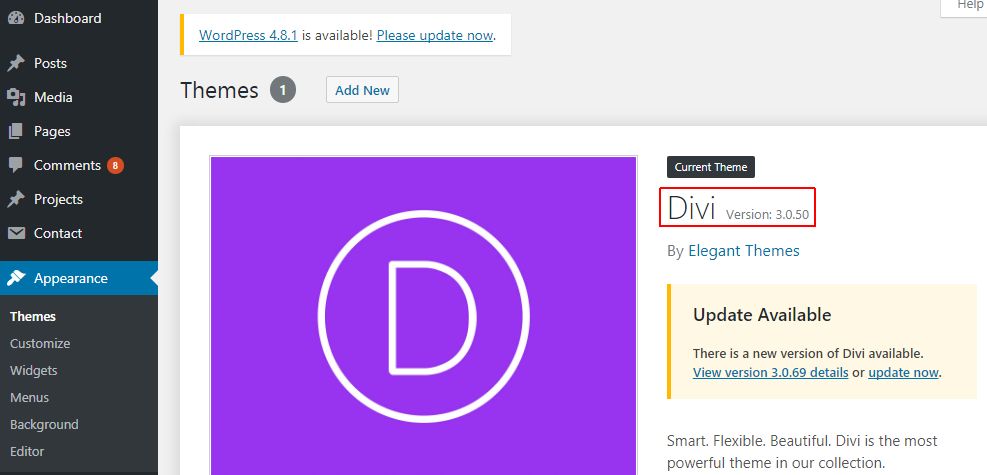
5. Install the themes (keep the same version for best compatibility)
For compatibility reason, it’d better to upload the theme files with the same version as existing one (at least major version).
If you are using free theme available at WordPress.org , you can download at https://wordpress.org/themes/
If you are using some commercial/premium (i.e. paid) theme, you may login to the corresponding vendor website and download it.
For example, ThemeForest , TemplateMonster , etc.
(In few circumstances, some customers may need to re-purchase the theme license if lost)
6. Install the plugins (preferably the same version for best compatibility)
For compatibility reason, it’d better to upload the plugin files with the same version as existing one.
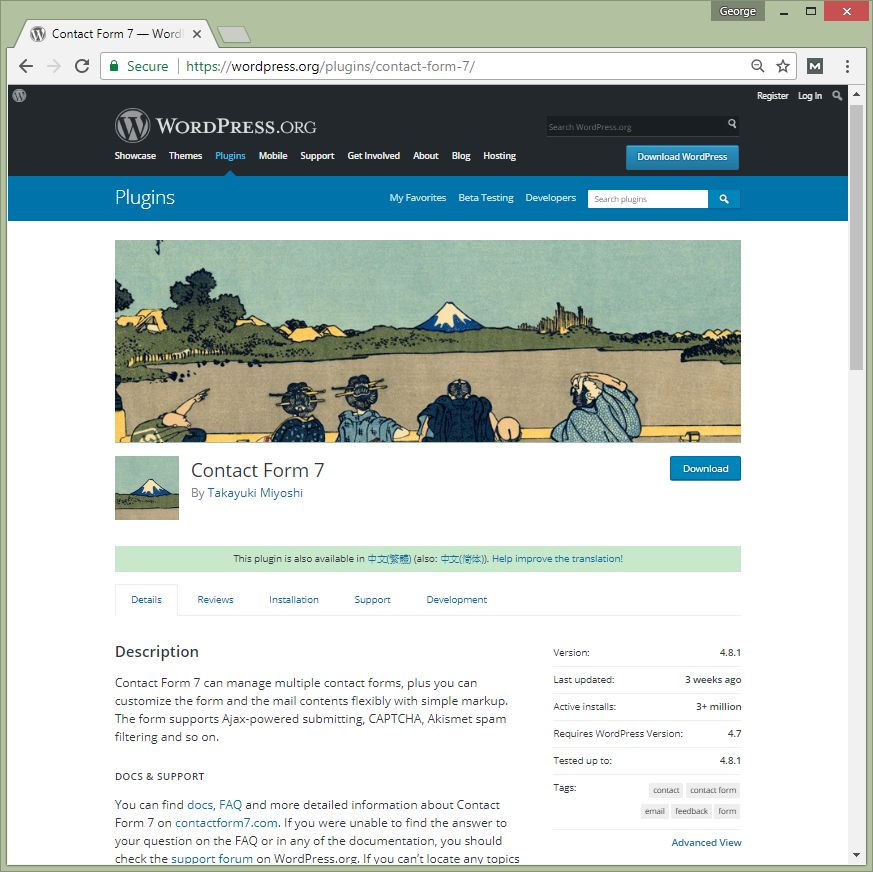
If you are using free plugins available at WordPress.org , you can visit at https://wordpress.org/plugins/
For each plugin, there is an “Advanced View”, and you can download archive version at the bottom.
If you are using some commercial/premium (i.e. paid) theme, you may login to the corresponding vendor website and download it.
For example, CodeCanyon etc.
(In few circumstances, some customers may need to re-purchase the plugin license if lost)
7. Upload the wp-content/uploads (Be careful)
This folder (/wp-contents/uploads) contains your website uploaded media files (e.g. jpg, gif, …)
It is necessary to re-upload those files from your infected source to the newly installed WordPress.
You need to inspect all files inside here to check any suspicious.
For example, any files with .php extension (404.php , admin.php , wp-files.php , wp-files.php5 , or simply .me.php , etc).
Also, you may use antivirus scanner to scan this folder before upload too.
If the upload contains malware files, then your newly “fixed” website can be re-infected easily.
8. Change wp-config.php back to the original database
9. Your website shall come up as usual
At this point, your WordPress website shall be able to show up without malware files (if /wp-contents/uploads/ is clean)
However, it probably is an outdated installation.
10. Make another backup
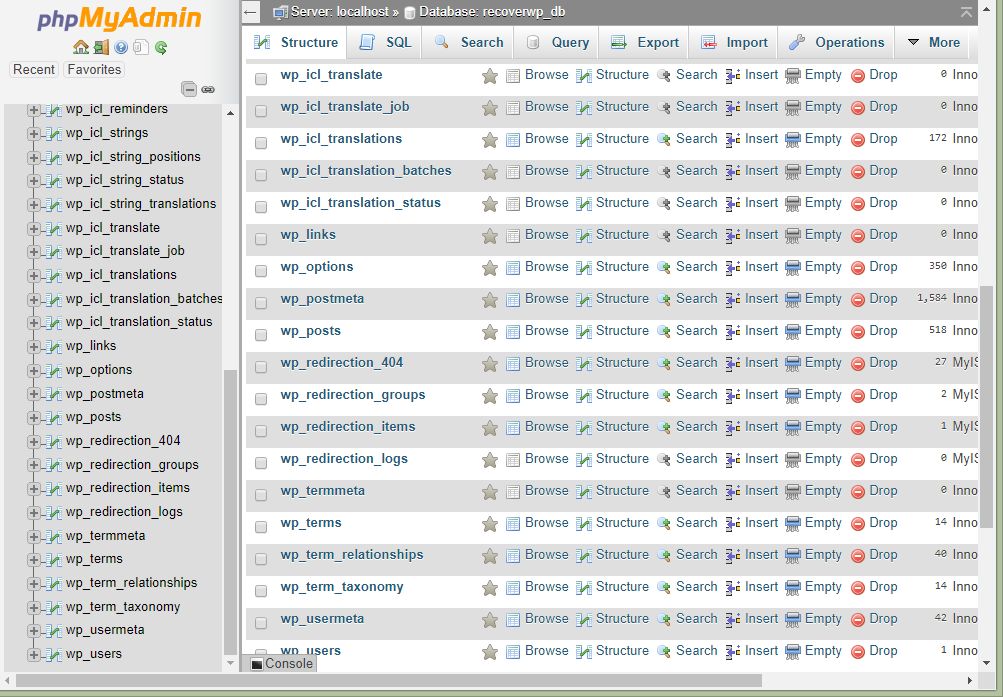
11. Check the database, for example, any suspicious WordPress users
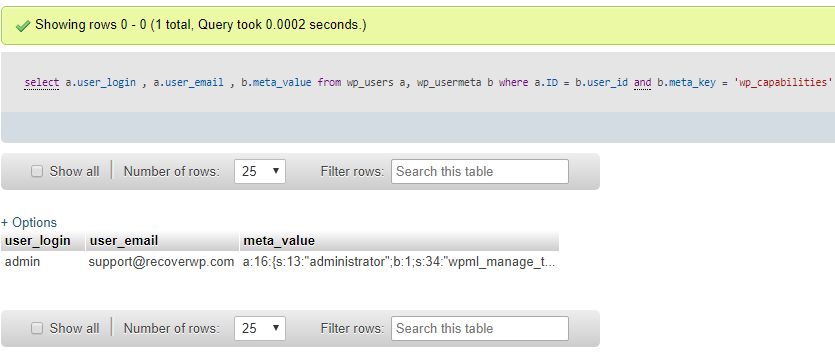
Login to phpMyAdmin, inspect the user tables, especially like wp_users for any suspicious (username, email, and its capabilities).
Capabilities means the role, i.e. he is an admin/editor/author/shop manager/…
in phpMyAdmin, you may use this SQL statement to fetch it
select a.user_login , a.user_email , b.meta_value from wp_users a, wp_usermeta b where a.ID = b.user_id and b.meta_key = ‘wp_capabilities’
12. Update WordPress configuration file (wp-config.php)
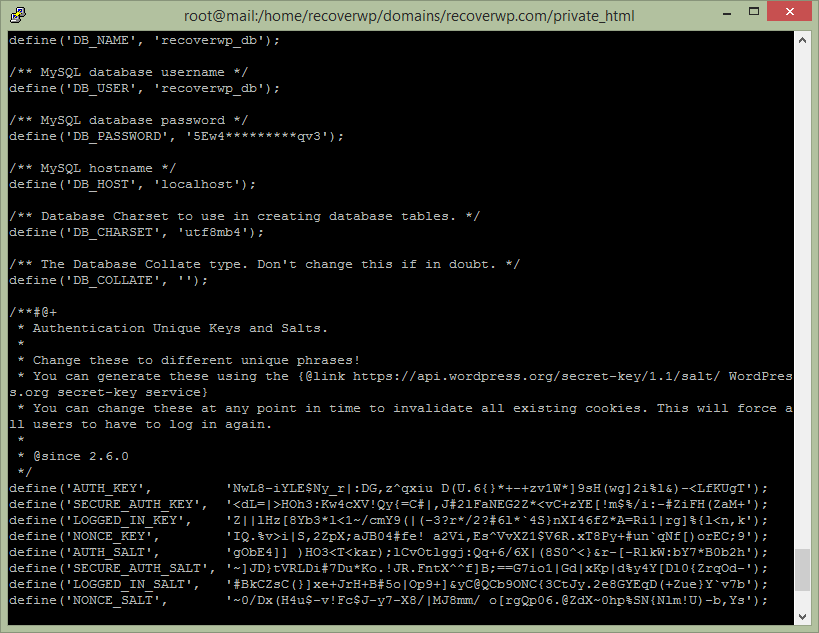
wp-config.php stores your database login information, and some of authentication keys.
As the previous malware files can get access on wp-config.php , it’d better to change MySQL database password, and reset the authentication keys.
Please consult web hosting on how to change MySQL database password. The, update wp-config.php → DB_PASSWORD
To change the authentication keys, visit https://api.wordpress.org/secret-key/1.1/salt/ , update (copy text and paste) wp-config.php → “Authentication Unique Keys and Salts.”
13. Change Password
For security reason, you shall consider to change the following passwords –
- Password of all WordPress admin, editors, and contributors.
- Website Control Panel Password (e.g. cPanel, Plesk, DirectAdmin, etc.)
- FTP Password
14. Remove Unnecessary Items
For security reason, it’d better to keep minimal but necessary components inside your WordPress website. For unnecessary items, you shall consider to remove them, to minimize attack surface area.
Some unnecessary items, for example, are –
- Inactive themes
- Deactivated plugins
- Inactive users
15. Update, update, and update
For security reason, keep your website application updated, to minimize the security threat.
Therefore, please update WordPress core, update Themes, and update plugins.
After update, remember to check any issues.
Generally, version contains 3 numbers. For example, for WordPress 4.7.5
4 = major version
7 = minor version
5 = bug fix (and/or security) release
In our experience, the change in the 3rd digit (e.g. from 4.7.4 to 4.7.5) is very safe to update (i.e. shall be no compatibility problem)
16. Make a final backup
Make a final backup, download it, keep it safe.
Also, you shall consider to have remote offsite backup regularly.
In future, in case of problem/emergency (e.g. due to human error, hardware failure, or being hacked), you can restore it.
At this point, if you are not sure how to start, you can find us for a WordPress Malware Removal service
About RecoverWP.com
RecoverWP.com is managed by web hosting professionals, who have been working on web hosting, WordPress website, security and vulnerabilities area since 2003.
Contact: (852) 3502-4863 | Email: support@recoverwp.com
Copyright 2015-2019 (c) Website Maintenance Service Limited